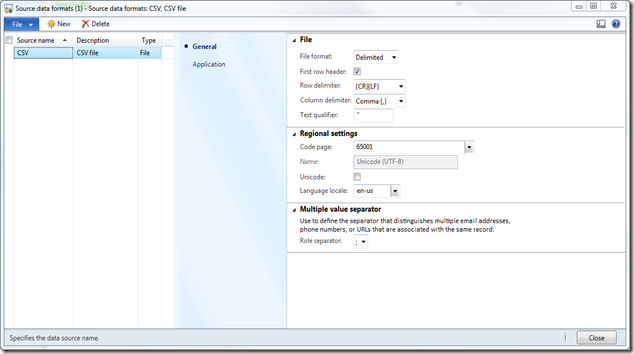
Writing Data to Excel file
How it works
1. Use SysExcelApplication class to create excel file.
2. Use SysExcelWorkbooks and SysExcelWorkbook to create a blank workbook(by default 3 worksheets will be available).
3. Use SysExcelWorkSheets to select worksheet for writing data.
4. SysExcelCells to select the cells in the excel for writing the data.
5. SysExcelCell to write the data in the selected cells.
6. Once you done with write operation use SysExcelApplication.visible to open
file.
static void Write2ExcelFile(Args _args)
{
InventTable inventTable;
SysExcelApplication application;
SysExcelWorkbooks workbooks;
SysExcelWorkbook workbook;
SysExcelWorksheets worksheets;
SysExcelWorksheet worksheet;
SysExcelCells cells;
SysExcelCell cell;
int row;
;
application = SysExcelApplication::construct();
workbooks = application.workbooks();
workbook = workbooks.add();
worksheets = workbook.worksheets();
worksheet = worksheets.itemFromNum(1);
cells = worksheet.cells();
cells.range('A:A').numberFormat('@');
cell = cells.item(1,1);
cell.value("Item");
cell = cells.item(1,2);
cell.value("Name");
row = 1;
while select inventTable
{
row++;
cell = cells.item(row, 1);
cell.value(inventTable.ItemId);
cell = cells.item(row, 2);
cell.value(inventTable.ItemName);
}
application.visible(true);
}
Reading Data from Excel File
static void ReadExcel(Args _args)
{
SysExcelApplication application;
SysExcelWorkbooks workbooks;
SysExcelWorkbook workbook;
SysExcelWorksheets worksheets;
SysExcelWorksheet worksheet;
SysExcelCells cells;
COMVariantType type;
int row;
ItemId itemid;
Name name;
FileName filename;
;
application = SysExcelApplication::construct();
workbooks = application.workbooks();
//specify the file path that you want to read
filename = "C:\\item.xls";
try
{
workbooks.open(filename);
}
catch (Exception::Error)
{
throw error("File cannot be opened.");
}
workbook = workbooks.item(1);
worksheets = workbook.worksheets();
worksheet = worksheets.itemFromNum(1);
cells = worksheet.cells();
do
{
row++;
itemId = cells.item(row, 1).value().bStr();
name = cells.item(row, 2).value().bStr();
info(strfmt('%1 - %2', itemId, name));
type = cells.item(row+1, 1).value().variantType();
}
while (type != COMVariantType::VT_EMPTY);
application.quit();
}
How it works
1. Use SysExcelApplication class to create excel file.
2. Use SysExcelWorkbooks and SysExcelWorkbook to create a blank workbook(by default 3 worksheets will be available).
3. Use SysExcelWorkSheets to select worksheet for writing data.
4. SysExcelCells to select the cells in the excel for writing the data.
5. SysExcelCell to write the data in the selected cells.
6. Once you done with write operation use SysExcelApplication.visible to open
file.
static void Write2ExcelFile(Args _args)
{
InventTable inventTable;
SysExcelApplication application;
SysExcelWorkbooks workbooks;
SysExcelWorkbook workbook;
SysExcelWorksheets worksheets;
SysExcelWorksheet worksheet;
SysExcelCells cells;
SysExcelCell cell;
int row;
;
application = SysExcelApplication::construct();
workbooks = application.workbooks();
workbook = workbooks.add();
worksheets = workbook.worksheets();
worksheet = worksheets.itemFromNum(1);
cells = worksheet.cells();
cells.range('A:A').numberFormat('@');
cell = cells.item(1,1);
cell.value("Item");
cell = cells.item(1,2);
cell.value("Name");
row = 1;
while select inventTable
{
row++;
cell = cells.item(row, 1);
cell.value(inventTable.ItemId);
cell = cells.item(row, 2);
cell.value(inventTable.ItemName);
}
application.visible(true);
}
Reading Data from Excel File
static void ReadExcel(Args _args)
{
SysExcelApplication application;
SysExcelWorkbooks workbooks;
SysExcelWorkbook workbook;
SysExcelWorksheets worksheets;
SysExcelWorksheet worksheet;
SysExcelCells cells;
COMVariantType type;
int row;
ItemId itemid;
Name name;
FileName filename;
;
application = SysExcelApplication::construct();
workbooks = application.workbooks();
//specify the file path that you want to read
filename = "C:\\item.xls";
try
{
workbooks.open(filename);
}
catch (Exception::Error)
{
throw error("File cannot be opened.");
}
workbook = workbooks.item(1);
worksheets = workbook.worksheets();
worksheet = worksheets.itemFromNum(1);
cells = worksheet.cells();
do
{
row++;
itemId = cells.item(row, 1).value().bStr();
name = cells.item(row, 2).value().bStr();
info(strfmt('%1 - %2', itemId, name));
type = cells.item(row+1, 1).value().variantType();
}
while (type != COMVariantType::VT_EMPTY);
application.quit();
}